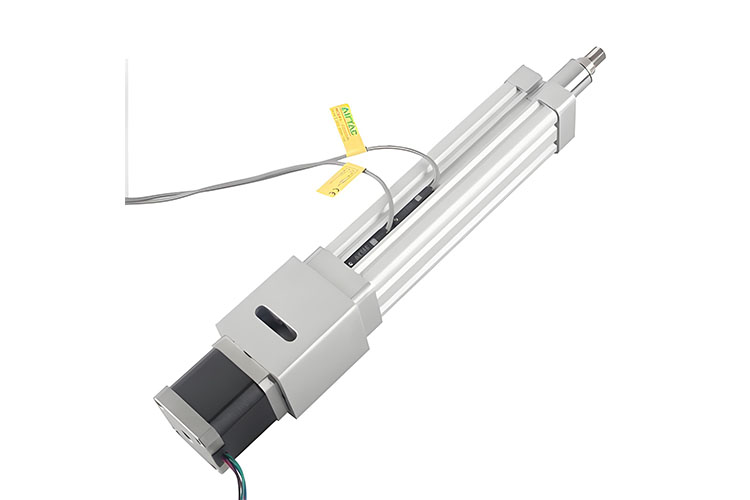
Understanding Electric Cylinders: The Foundation of Modern Motion
Picture a world at your fingertips. With a single press, machines move with perfect precision. That’s the promise of electric cylinders—the quiet power behind automation.
An electric cylinder turns electric energy into a straight push or pull. This is called linear motion. You find these cylinders in many places, from car factories to labs. Inside, they utilize a motor, a screw drive (like a round screw, roller screw, or lead screw), a rod or slider, a real estate, and comments components. The job is easy: make points relocate in and out, backwards and forwards, fast or slow-moving.
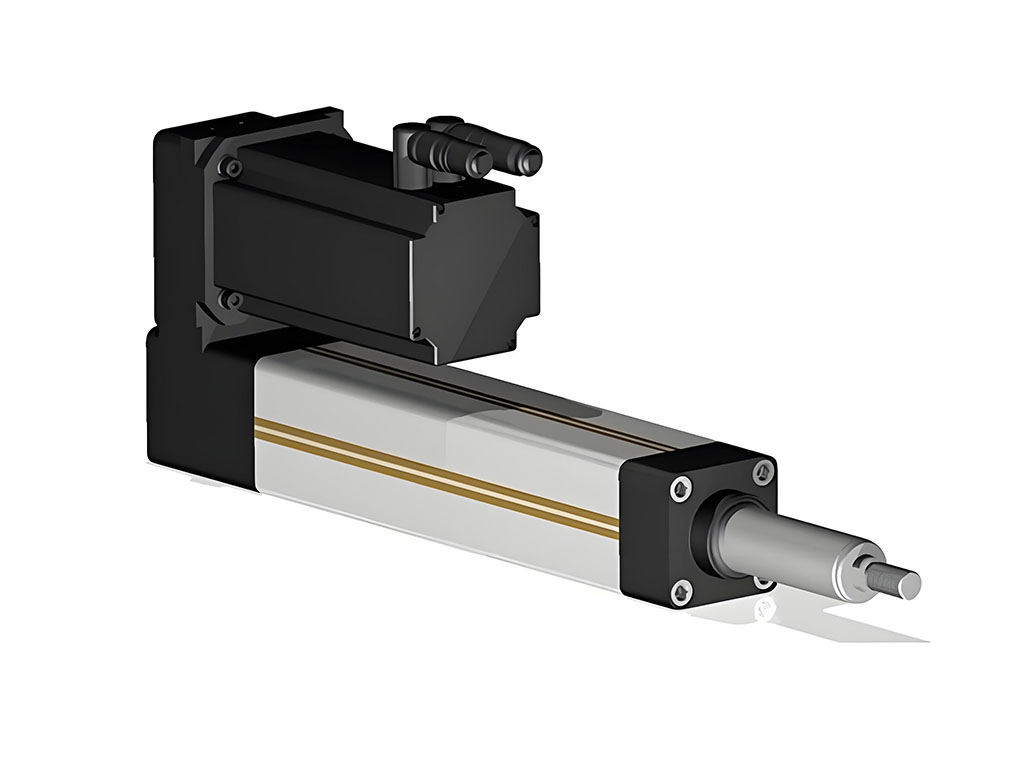
Why does this issue to you? Automation is anywhere. Whether you’re a student, an engineer, or simply curious, understanding how electric cylinders work opens up doors to smart services in your home, in industry, and past.
Exactly How Electric Cylinders Work: Unpacking the Mechanics
The Principle of Linear Motion Conversion
How does a simple button press move a heavy door or lift a lab sample? It all starts with a motor that spins. That spin must somehow travel in a straight line. That’s where the screw drive comes in. The motor turns the screw. The screw pushes or pulls a rod. Now you get smooth, straight movement—no fuss.
Drive Mechanisms: Ball Screw, Roller Screw, and Lead Screw Compared
Not all drives are equal. Here’s how they stack up:
- Ball Screw: Small balls run inside the screw, making motion smooth and quickly. This gives high performance and long life, yet it can set you back a bit a lot more. Helpful for jobs that need constant, strong motion– believe accuracy assembly lines.
- Roller Screw: Tiny rollers, not balls, carry the force. This type works even better under heavy loads and lasts even longer. It’s ideal for tough spots, but it’s pricier.
- Lead Screw: No balls or rollers, just a direct path. It’s simple and cheaper but can wear out faster and may be slower.
Selecting depends on your needs—speed, load, budget, or lifetime. For more, check our Ball Screw Actuators and Lead Screw / Acme Screw Actuators pages.
Motor Integration & Control: Servo vs. Stepper and Feedback Loops
What’s behind the motion? Motors! Two big types rule here:
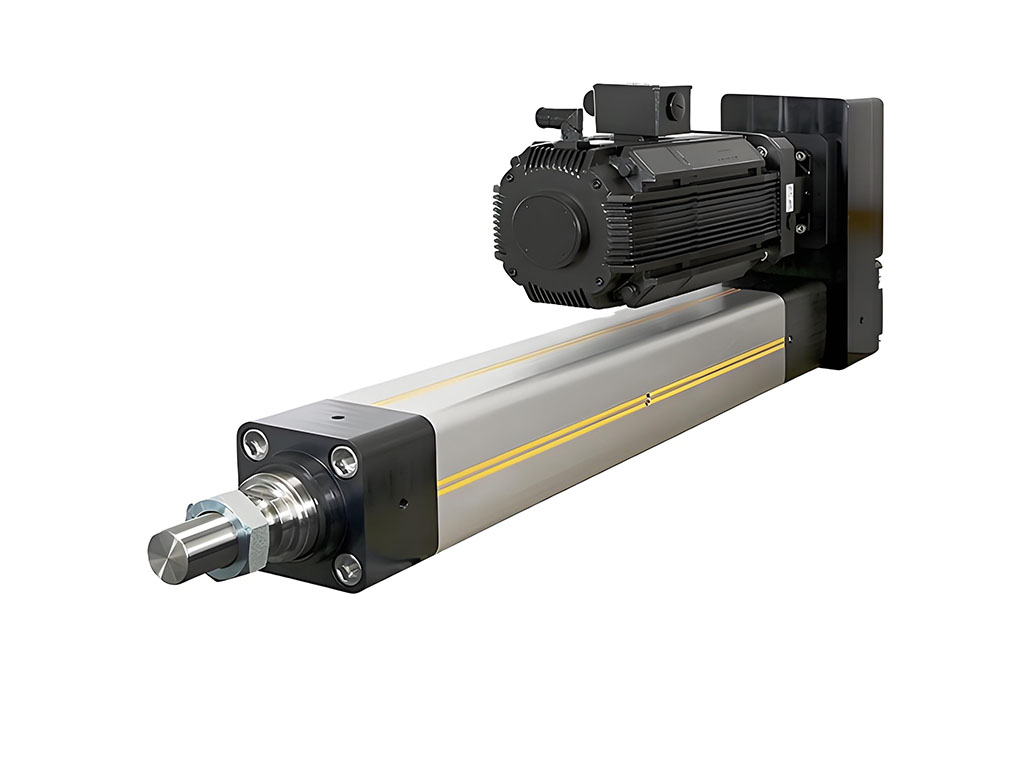

- Servo motors are smart. They know exactly where to go and how fast. They’re best for jobs that need pinpoint precision.
- Stepper motors work in steps. They’re simpler and cost less, but may slip under big loads.
Feedback devices like encoders give the motor a sense of touch. They tell the system if it hit the right spot. If not, the system corrects itself. This loop makes every move sharp and safe.
When it comes to control, you need an electronic brain. It’s often a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a simple remote box. For tight jobs, add a Human-Machine Interface (HMI) for easy setup.
Kinds Of Electric Cylinders & Their Diverse Applications
Rod-Style vs. Rodless Electric Cylinders (Linear Actuators).
- Rod-style cylinders: Picture a stick poking out. They fit where you need to push something out or pull it back. They’ll need something strong to hold up loads.
- Rodless cylinders (linear actuators): These don’t have an outside rod. The load rides right on the moving piece—saving space, perfect for long reaches in tight spots. Check options at Rodless Actuators and Electric Linear Actuators.
Exploring Specialized Electric Cylinder Designs
Sometimes the task is unique. That’s when you turn to:
- Integrated motor cylinders: All-in-one, quick to set up.
- High-force models: Tackle heavy machines or press jobs.
- Miniature versions: Perfect for small devices or medical tools.
- Washdown and explosion-proof types: Go where safety and cleanliness are top priorities.
Where Electric Cylinders Shine: Real-World Applications
Electric cylinders lift, push, and position in places like:
- Industry: Move products on an assembly line, sort boxes, or fill bags.
- Medical: Precise dosing machines, lab robots, even hospital beds.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Test brakes and simulate driving forces.
- Food, Energy, and Entertainment: Control gates, presses, and even amusement rides.
Their mix of speed, strength, and clean operation makes them a go-to tool in automation. See more at Industrial Linear Actuators and Industrial Automation Actuators.
Electric vs. Fluid Power: Advantages & Disadvantages of Electric Cylinders
The Undeniable Benefits of Electric Cylinders
Why switch to electric cylinders?
- Precision: Hit the same spot every time—with accuracy down to ±0.01mm (source).
- Energy efficiency: Use up to 80% less power than pneumatics or hydraulics (source). That means savings and greener operations.
- Clean operation: No leaks, no need for noisy pumps or compressors.
- Control: Change speed, position, or force on the fly.
- Easy install: Fewer parts, less mess, less hassle.
Addressing the Limitations: What to Consider
Electric cylinders do have limits:
- Initial price: They cost more upfront than simple fluid systems.
- Peak force: Not as strong as big hydraulic cylinders.
- Programming know-how: Setting up complex moves takes some skill.
Strategic Comparison: Electric, Hydraulic, and Pneumatic Technologies.
| Feature | Electric Cylinder | Hydraulic Cylinder | Pneumatic Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Very high | Medium | Low |
| Force | Medium to high | Highest | Low to medium |
| Speed | Variable, fast options | Fast | Very fast |
| Energy Use | Very low | High | High |
| Cleanliness | Very clean | Risk of fluid leaks | Oil-free but dusty |
| Upkeep | Very low | High | Medium |
Need assistance choosing? Check out your must-haves– accuracy, cost, upkeep– and select what suits.
Selecting the Right Electric Cylinder: A Step-by-Step Guide.
Defining Your Application Requirements
Begin with your needs:
- Force: How heavy is your load? Is it pushing, pulling, or both?
- Speed: How quickly must it move?
- Stroke: How far does it need to travel?
- Duty cycle: Will it run all day, or simply in ruptureds?
- Accuracy: How close must it hit the target every time?
Environmental and Mechanical Considerations.
- Temperature level and moisture: Must it work in the rainfall, warm, or cold?
- IP rating: Need dust or water protection?
- Space: Big area or tight corner?
- Mounting: Will it go sideways, up high, or upside down?
Electrical & Control System Integration
- Power: Does your site have enough supply?
- Controls: Will it talk to your PLC? Are you using a remote or an HMI for tweaks?
- Software: Do you need custom settings, or off-the-shelf programming?
Explore Servo Motor Actuators for smart choices.
Setup, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting for Longevity.
Ideal Practices for Installation and Commissioning.
Get the basics right. Align and mount the cylinder square. Wire with care. Follow start-up steps from the manual. Run test cycles to check.
Making Sure Long Lifespan: Routine Maintenance and Predictive Approaches.
Remaining on leading means:.
- Lubricate if needed.
- IExamine for wear, loosened screws, or strange resonances.
- Use smart sensors to monitor heat or changes—predict and stop problems before they start.
Common Issues and Basic Troubleshooting
Spot issues fast:
- Is it noisy or getting hot? Check mounting, wires, and settings.
- Off-target moves? Recalibrate or check feedback devices.
- Still stuck? Consult the manual or reach out to experts at Jimi.
Safety Guidelines for Operating Electric Cylinders
- Always power down before working.
- Add guards to pinch points.
- Know and use emergency stop controls.

Future Trends and Innovations in Electric Cylinder Technology
The future? Even smarter, smaller, and stronger. We see:
- Industry 4.0: Connect cylinders to smart factory networks for real-time tweaks.
- Miniaturization: Smaller but mightier for robots and medical gear.
- Better materials: Lighter but tougher designs.
- AI and self-optimization: Systems that predict their own needs.
- Special uses: Touch feedback, more lifelike robots, even space tech.
Key Data Insights on Electric Cylinders: The Numbers Speak
- Energy savings: Slash use by as much as 80% (source).
- Precision: Repeatable positioning of ±0.01mm saves time and cuts waste (source).
- Ownership costs: Even if you pay more at the start, you may save 30–50% down the line (source).
- Market growth: This market will reach $14.5 billion by 2030, growing over 6% a year (source).
- Cleanliness: No leaks, no air mess—better for food, labs, and cleanrooms (source).
FAQ: Your Electric Cylinder Questions Answered
What is an electric cylinder and how does it work?
It’s a device that turns electric power into straight motion using a motor and a screw drive.
What’s the distinction in between an electrical cyndrical tube and a direct actuator?
All electric cyndrical tubes are linear actuators, yet not all linear actuators have the same form.
Electric vs hydraulic cylinder: Which is better?
Electric for accuracy and clean use. Hydraulic for very high force.
What are the main advantages of using electric cylinders?
They are precise, clean, easy to control, and need less upkeep.
How do I select the correct electric cylinder for my application?
Know your load, speed, stroke, duty cycle, and the working environment.
Are electric cylinders energy efficient?
Very! They can save up to 80% more energy than other systems.
Conclusion & Next Steps
From simple moves to smart factories, electric cylinders deliver. We at Jimi have spent years building reliable, precise solutions for every job. Our strength lies in our experience—helping customers turn ideas into moving reality.
Ready to bring effortless control to your line or project? Contact Jimi, the preferred solution provider for expertise that moves you forward. Take the first step towards smarter automation—because with us, the future is in motion.







